https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.04710
Expressive-VC: Highly Expressive Voice Conversion with Attention Fusion of Bottleneck and Perturbation Features
Voice conversion for highly expressive speech is challenging. Current approaches struggle with the balancing between speaker similarity, intelligibility and expressiveness. To address this problem, we propose Expressive-VC, a novel end-to-end voice convers
arxiv.org
해당 논문을 보고 작성했습니다.
Abstract
highly expressive speech에 대한 voice conversion은 어려운 문제입니다. 최근 방식들은 speaker similarity, intelligibility, expressiveness 사이 밸런스를 맞추는 데 어려움을 겪고 있습니다. 이러한 문제를 해결하기 위해, 저자들은 Expressive-VC라는 neural bottleneck feature (BNF) approach와 information perturbation approach의 장점을 모두 사용하는 새로운 end-to-end voice conversion framework를 제안합니다. 구체적으로 BNF encoder와 Perturbed-Wav encoder를 이용해 linguistic feature와 para-linguistic feature를 학습하는 content extractor를 구축했습니다. robust pre-traiend ASR model에서 BNFs를 구하고 signal perturbation 이후 perturbed wave는 speaker-irrelevant 하게 됩니다. 이후 attention mechanism을 이용해 linguistic and para-linguistic feature를 fuse 합니다. 이때 speaker-dependent prosody feature를 attention query로 사용합니다. speaker-dependent prosody feature는 source speech의 normalized pitch, energy와 target speaker embedding을 input으로 사용하는 prosody encoder의 result입니다. 마지막으로 decoder는 integrated feature와 speaker-dependent prosody feature를 이용해 converted speech를 생성합니다.
Introduction
인간의 음성에 포함된 정보는 크게 linguistic, para-linguistic, non-linguistic 요소로 나눌 수 있습니다. linguistic은 언어, para-linguistic은 rhythmic-emotional, non-linguistic은 speaker identity를 나타냅니다. 또한 숨소리, 웃음, 울음과 같은 non-verbal sounds도 중요한 역할을 합니다. voice conversion은 주어진 speech의 speaker-related information을 바꿔 linguistic, para-linguistic, non-verbal sound는 보존한 채로 다른 사람의 목소리처럼 들리는 speech를 생성하는 기술입니다.
voice conversion에서 source audio에서 speaker-relevant and speaker-irrelevant information을 분리하고 speaker-irrelevant information을 target spaeker에 적용하는 것이 주요 task입니다. speech에서 해당 요소들은 강하게 얽혀있어 완전히 분리하는 것은 어렵습니다.
몇몇 disentanglement approach들은 specific module, loss or learning algorithm 등 voice conversion model의 세밀한 design에 의존하여 학습된 feature가 linguistic content 또는 speaker identity를 나타내도록 constraint 합니다. 예를 들어 vector quantization (VQ), adaptive instance normalization, gradient reversal layer (GRL)는 학습된 feature에 pure linguistic related feature가 존재하지만 speaker-related information이 없도록 만듭니다. mutual information (MI) loss는 학습된 feature에 speaker information and linguistic information 사이 연관성을 minimize하는데 사용됩니다. 이러한 방식들은 'target speaker의 음색을 유지하려면 expressiveness를 일정 부분 희생해야 하며, source speaker의 timbre가 target speaker에게 전달된다면, converted speech가 source speaker의 목소리 또는 섞인 목소리로 들리게 된다'라는 딜레마에 직면하게 됩니다.
몇몇 연구들은 voice conversion model 외에서 또는 이전에 따로 disentanglement를 수행합니다. decoupled feature를 input으로 받는다면 VC model이 더 쉽게 disentanglement를 수행할 수 있게 됩니다. 이러한 방식으로 phonetic posteriorGrams (PPGs)와 neural network bottleneck features (BNFs)을 주로 사용합니다. 구체적으로 BNFs는 neural network bottleneck layer에서 node의 activation set이고, PPGs는 neural network로부터 phonetic posterior probabilistic vector sequence를 stack 하여 구해집니다. BNFs와 PPGs 둘 다 linguistic 정보가 풍부하고 speaker-independent and noise-robust 하다고 증명되어 있는 well-trained automatic speech recognition (ASR) system에서 구해집니다. PPGs/BNFs을 intermediate representation으로 사용하여 voice conversion processing이 speech-to-BNFs/PPGs module, BNFs/PPGs-to-speech module로 표현됩니다. 이러한 방식은 source speech의 linguistic information을 target speech에 안정적으로 적용할 수 있습니다. BNFs/PPGs에 대부분의 linguistic information이 존재하기 때문에, converted speech는 source speech의 expressivenss를 손실하게 됩니다. pitch와 같은 추가적인 prosody feature를 사용하여 이러한 문제를 완화할 수 있습니다.
최근에는 information perturbation을 이용해 prior에서 speaker timbre를 제거하여 voice conversion을 수행합니다. informationperturbation의 basic idea는 신호 처리를 통해 speech에 있는 불필요한 정보를 제거하여, neural network가 필수적인 정보를 효과적으로 학습할 수 있도록 만드는 것입니다. 구체적으로 information perturbation은 source speech에 있는 speaker-related information을 제거하고 content encoder를 통해 linguistic information을 modeling합니다.
speaker perturbation 이후에도 speech에는 emotional information과 같은 para-linguistic이 여전히 존재할 수 있습니다. 그래서 이러한 방식의 voice model은 위에서 언급한 speaker similarity and expressiveness 사이 trade-off를 해결할 수 있습니다. 따라서 information perturbation을 사용하면 source speech의 expression을 유지하면서 target speaker의 timbre를 반영하는 converted speech를 생성할 수 있습니다. 하지만 perturbation parameter를 empirical 하게 선택되기 때문에, 이러한 방식들은 converted speech의 intelligibility and quality의 안정성이 떨어질 수 있습니다.
highly expressive source speech voice conversion을 위해, 이 논문에서는 Expressive-VC를 제안합니다. 이는 neural bottleneck feature approach와 information perturbation approach의 장점 모두 사용한 새로운 end-to-end voice conversion method framework입니다. BNF encoder, perturbed-wav encoder를 이용해 content extractor를 구성하고 linguistic and para-linguistic feature를 학습합니다. BNF는 robust pre-trained ASR model을 통해 구해지고 perturbed wave는 signal perturbation 이후 speaker-irrelevant 한 output을 나타냅니다. 그다음 scaled dot-product attention mechanism을 통해 linguistic and para-linguistic feature를 fuse 합니다. target speaker embedding과 source speech의 normalized pitch and energy를 input으로 사용하는 prosody encoder에서 구한 speaker-dependent prosody feature를 attention query로 사용합니다. 마지막으로 decoder가 fused feature와 speaker-dependent prosody feature를 이용해 converted speech를 생성합니다.
Proposed Approach
expressive voice conversion을 위해, bottleneck feature (BNF)에 embed 된 robust linguistic information과 speaker-attribute-perturbed wave (Perturbed-wav)에 존재하는 풍부한 para-linguistic information을 fusing 하여 Expressive-VC system을 design 하였습니다.

위 그림의 (a)처럼 Expressive-VC는 encoder-decoder architecture base이며, 크게 content extractor, prosody encoder, decoder, discriminator로 구성됩니다.
Content Extractor
content extractor는 BNF encoder, Perturbed-Wav encoder, fusion module로 구성됩니다. BNF encoder는 source speech에서 linguistic feature를 학습하고 Perturbed-Wav encoder는 para-linguistic feature를 학습합니다. 그다음 fusion module은 두 type의 feature를 fuse 하여 converted speech의 expressivity와 reasonable intelligibility를 향상시켰습니다.
- BNF & Perturbed-Wav Encoders
BNF encoder는 BNF를 input으로 받아 source speech의 linguistic embedding Hb를 output 합니다. Perturbed-Wav encoder는 perturbed wave를 input으로 받아 source speech의 para-linguistic-related embedding Hw를 output 합니다. Hb,Hw∈RT×F이고, T는 sequence length를 나타내고 F는 embedding의 dimension을 나타냅니다. pre-trained ASR model을 통해 source waveform Y에서 BNFs를 추출합니다. 3가지 신호 처리 함수를 통해 perturbed wave를 구합니다. pitch randomization (pr), formant shifting (fs), parametric equalizer를 이용한 random frequency shaping (peq)를 사용합니다. pitch randomization function은 pitch와 scale을 shift 하고 formant shifting function은 formant를 shift 하여 source waveform의 speaker timbre를 변환합니다. frequency band의 energy를 변경하여 parametric equalizer function이 speaker-relevant information을 제거합니다. 요약하면, speaker perturbation process는 다음과 같이 나타낼 수 있습니다.

perturbed wave는 general linguistic and para-linguistic pattern은 유지하면서 speaker-irrelevant information이 존재합니다.
- Feature Fusion Module
source speech에서 linguistic and para-linguistic information 모두 포항하고 있는 robust and rich content representation을 얻는 것은 VC task에서 중요합니다. BNFs는 linguistic-rich 하지만 speech의 대부분의 expessivity가 손실되었다고 알려져 있습니다. 반면에 speaker-perturbed wave에서 추출한 embedding은 speech의 풍부한 표현력이 존재할 수 있습니다. 그래서 간단한 덧셈이나 conatenation으로 두 feature를 결합하는 것은 직관적인 idea입니다. 하지만 저자들은 시간에 따라 linguistic and para-linguistic aspect들의 contribution이 다르다고 생각하며, fusion은 dynamic 하게 이뤄져야 된다고 생각합니다. 예를 들어 숨소리와 같은 non-verbal sound는 BNF embedding의 contribution은 낮고 Perturbed-wav embedding의 contribution은 높을 수 있습니다. ASR의 acoustic model에서는 이러한 non-verbal sound를 명시적으로 modeling 하지는 않습니다.
dynamic fusion을 위해, 저자들은 linguistic feature Hb와 para-linguistic feature Hw를 효과적으로 결합하는 attention-based fusion module을 제안합니다. 위 그림의 (b)처럼 Hb,Hw를 concatenate 한 결과를 key, value K∈RT×2×F로 사용합니다. prosody encoder의 output Hp는 query Q∈RT×F×1로 사용되어 Hb,Hw에 있는 linguistic and para-linguistic information과 integrate 됩니다. 다시 말해 source speech의 general prosody pattern (source speaker timbre removed)을 이용해 두 branch를 weight fusion 합니다. attention mechanism 이후에 scaled dot-product operation을 이용해 유사도를 측정합니다. 전체 process는 다음과 같습니다.

Hf∈RT×F는 fusion module의 output입니다.
Prosody Encoder
source speech에서 prosody를 잘 보존하고 target speech와 높은 speaker similarity를 얻기 위해, prosody encoder를 이용해 speaker-related prosody representation을 학습합니다. source speech Y에서 pitch (f0)와 energy (e)을 추출하고 z-score normalization을 진행해 source speaker의 timbre에서 pitch를 제거합니다. 이를 통해 speaker-independent prosody를 얻게 됩니다. 그다음 target speaker embedding을 conditional information으로 사용하여 conditional layer normalization (CLN)을 통해 target speaker-related prosody feature Hp를 생성합니다.
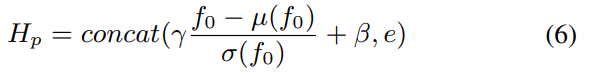
위 식에서 λ,β는 speaker embedding에 대한 scale and bias vector이고 μ(f0),σ(f0)는 utterance level의 f0의 평균과 분산을 나타냅니다. Hp는 위에서 말했던 fusion module의 attention query로 사용되고 content extractor ouput과 함께 decoder에 feed 됩니다.
Decoder and Discriminator
source speech의 input과 target speaker identity를 이용해, 추가적인 vocoder 없이도 waveform을 reconstruct 합니다. 저자들은 HiFi-GAN을 generator로 사용합니다.
Training Strategy for Forcing Feature Fusion
이상적으로 fusion model은 Hb에서 linguistic information을 학습하고 Hw에서 para-linguistic information을 추출하여 학습합니다. 하지만 BNFs은 perturbed waveform보단 linguistic information과 더 연관되어 있기 때문에, BNF encoder에서 linguistic information을 학습하는 것이 Perturbed-wav encoder에서 학습하는 것보다 더 쉽습니다. 결과적으로 fusion module이 BNFs에서 추출된 linguistic information Hb에 focus 하고 perturbed-wav encoder는 잘 활용하지 않는 경향을 보입니다.
더 나은 feature fusion을 위해, Perturbed wav encoder의 수렴 속도와 context extraction 성능이 학습할 때 보장되어야 합니다. 이를 위해, 학습할 때는 fusion module을 우회하고 Hw,Hp를 더하여 바로 decoder에 feed 하여 waveform을 reconstruct 합니다. 이러한 학습을 통해, Perturbed-wav encoder는 직접적으로 waveform reconstruction로 guide 되고 빠르게 최적화됩니다.
Experiments
Experimental Setup
저자들은 NANSY와 같은 perturbation coefficient를 사용하여 formant shifting, pitch randomization, random frequency shaping을 적용했습니다. 그리고 speed augmentation을 사용해 다양한 prosody diversity를 사용했습니다. 학습할 때 augmented and original waveform을 VC model에 feed 하였습니다. ASR system은 conformer-based model이며, WeNet toolkit을 이용해 구현하였습니다. BNF encoder는 2개 convolution layer와 layer normalization으로 구현하였습니다. Perturbed-wav encoder는 4개 convolution layer로 구성하였습니다. 그리고 각각 뒤에 layer normalization을 추가하였습니다. 저자들은 BNF-VC, Perturb-VC, AGAIN-VC와 비교를 진행했습니다.
Objective Analysis
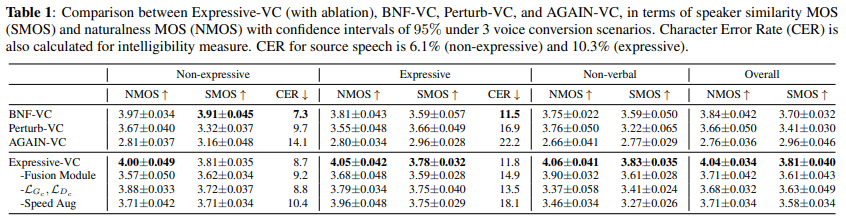
CER 결과는 위와 같습니다. AGAIN-VC가 가장 높은 CER을 기록했으며, 가장 좋지 않은 intelligibility를 기록했습니다. 하지만 저자들의 model은 BNF-VC와 유사한 성능을 보이며, source speech와 비교해도 소폭 상승이 있었습니다.
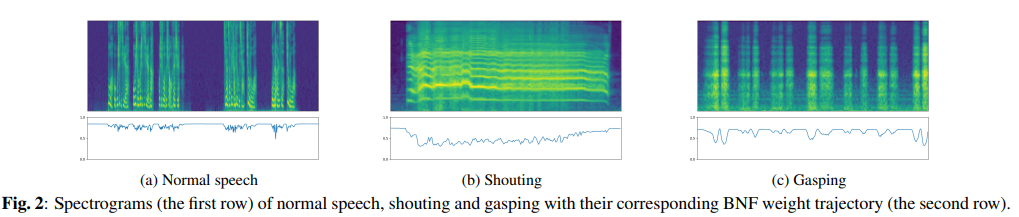
저자들은 source speech로 normal, shouting, gasping speech를 사용하여 mel-spectrum과의 attention weight를 계산했습니다. weight curve는 0 ~ 1 사이 값이며, 값이 작을수록 perturbed waveform에서 추출된 Hw가 더 많이 반영되는 것을 의미합니다. (a)를 보면 normal speech에서는 Hb가 더 많이 반영되는 모습을 보여줍니다. 반대로 shouting과 gasping은 Hw가 더 많이 반영되는 모습을 보여줍니다. 특히 (b)를 보면 시간이 지나면서 값이 변화하는 것을 볼 수 있으며, 시간에 따라 Hb,Hw가 동적으로 조정되는 것을 의미합니다.
- Pitch Correlation
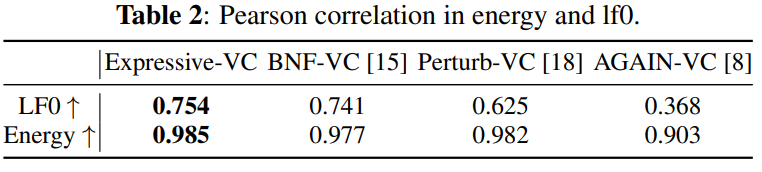
source and converted speech의 energy and pitch Pearson correlation coefficient를 계산했습니다. 더 높은 Pearson correlation coefficient를 보인다면 더 높은 predicted prosodic attribute accuracy를 보이는 것을 의미합니다. 실험 결과는 위와 같습니다. 저자들이 제안한 system이 가장 높은 lf0 and energy correlation을 보여줍니다. 즉 저자들이 제안한 system이 source speech의 expressive attribute를 더 잘 유지할 수 있다는 것을 의미합니다.
Conclusion
이 논문에서 저자들은 Expressive-VC을 제안합니다. source speech에서 linguistic and para-linguistic information을 유지하는 것의 어려움 때문에 target speaker의 timbre으로의 voice conversion task가 어렵습니다. 이를 위해 저자들은 multiple feature fusion을 제안합니다. bottleneck feature approach와 signal perturbation approach 장점 모두 이용하는 method입니다.



